Terrorism Charges – What They Mean and How They Work
If you’ve ever seen the news headline "terrorism charges" and felt confused, you’re not alone. Most people think it’s a vague term that only applies to big‑scale attacks, but the law actually defines it much more narrowly. In plain English, a terrorism charge is an accusation that someone has used or threatened violence to influence a government or intimidate a civilian population.
First off, the police don’t throw this label around lightly. In the UK, the Terrorism Act 2000 lists specific acts that count as terrorism, like bombings, hacking, or financing extremist groups. When prosecutors decide to bring a terrorism charge, they must prove not only the violent act but also the intent to create fear or coerce authorities.
How a Terrorism Case Moves Through the Courts
Once the police gather enough evidence, they hand the case to the Crown Prosecution Service (CPS). The CPS decides whether there’s a realistic chance of conviction and whether it’s in the public interest to prosecute. If they say yes, the suspect is charged and will appear before a magistrate’s court for an initial hearing.
At that hearing, the judge decides if there’s enough evidence for a trial. Most serious terrorism cases skip the magistrates and go straight to the Crown Court, where a jury decides guilt. The trial can involve secret evidence, special advocates, and sometimes closed sessions to protect national security.
Your Rights if You Face Terrorism Charges
Being charged with terrorism doesn’t strip you of basic rights. You still have the right to a solicitor, the right to remain silent, and the right to a fair trial. However, there are extra layers: you might be subject to extended police detention (up to 28 days), and some evidence may be disclosed only to a special advocate who can’t speak to you directly.
It’s crucial to get a lawyer experienced in counter‑terrorism law. They’ll know how to challenge secret evidence, request full disclosure, and argue whether the police overstepped any procedural rules. Even if the evidence is strong, a skilled solicitor can negotiate reduced charges or alternative sentencing.
Penalties for terrorism convictions are severe. Depending on the offense, sentences range from several years to life imprisonment. The courts also consider aggravating factors like planning, leadership roles, or targeting civilians. On the flip side, mitigating factors—such as cooperation with authorities or a genuine lack of intent—can lower the sentence.
Beyond prison, a terrorism conviction can lead to additional restrictions: travel bans, loss of voting rights, or being placed on a monitoring list after release. These measures aim to reduce any future risk but can have a lasting impact on everyday life.
What’s the takeaway? Terrorism charges are a heavy legal hammer reserved for acts that threaten public safety and national stability. If you or someone you know is facing such a charge, don’t wait—seek specialized legal help right away and understand the process step by step.
Understanding the basics helps you navigate the system, protect your rights, and make sense of the headlines. Stay informed, stay aware, and remember that even the most serious accusations come with legal safeguards designed to keep the process fair.
9
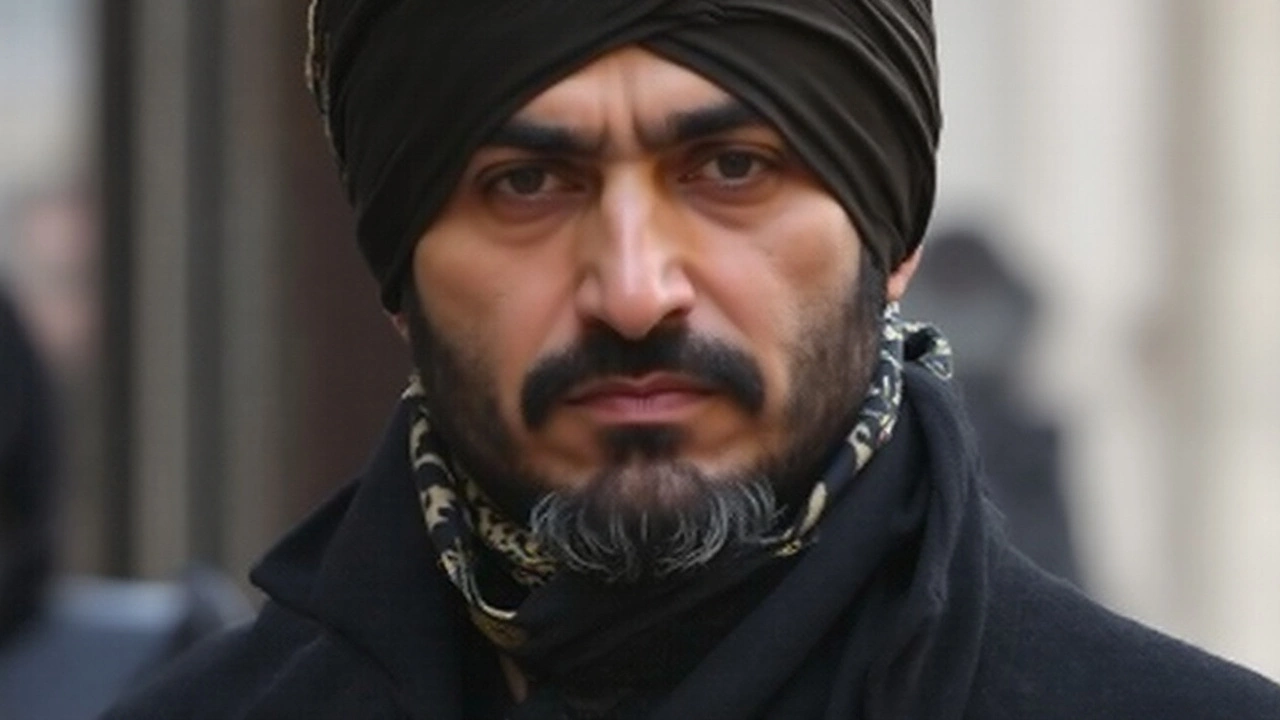

Haroon Aswat in New York court after extradition over Oregon camp plot
British suspect Haroon Aswat appeared in a Manhattan federal court on charges tied to plans for a terrorist training camp in Oregon. His case took years of legal fights across two continents, including a European human rights ruling over U.S. prison conditions and mental health care. He pleaded guilty in 2015, received a 20-year sentence, and was deported to the UK in 2022.